The atmospheric temperature decreases with height. But sometimes, the opposite happens: the bottom of the valleys registers colder temperatures than the summits of the mountains. This phenomenon is a consequence of the thermal inversion or inversion of temperature. We analyze What is thermal inversion and how it is related to pollution.
Why does thermal inversion occur?
To describe what is thermal inversion and why it is produced, it is first necessary to refer to the normal operation of the atmosphere.
Under normal conditions:
- During the day, the sun heats the Earth’s surface, which releases the heat little by little, heating the air from the adjacent atmosphere.
- This warmer air has a lower density, that is, it weighs less, which facilitates its ascent through the different layers that form the Earth’s atmosphere (the rise of a hot air balloon exemplifies this phenomenon very clearly).
- As it rises, the hot air cools and acquires greater density or weight, which causes gravity to attract it more strongly and displace the hot air closer to the Earth, generating a convective movement.
But during the long cold winter nights and in conditions of atmospheric stability such as those presented by the anticyclones (clear skies, little wind, etc.), this normal operation tends to break down.
How is this process produced?
Thermal inversion is a natural phenomenon that involves a change in the normal tendency of the air to cool down with altitude and that runs as follows:
- During the night, the earth’s surface cools quickly, transmitting that cold to the atmosphere closest to the ground.
- This layer of air has a lower temperature than the immediately higher one, that is, both have different densities, which prevents mixing.
- The thermal inversion is usually corrected as the sun reheats the earth’s surface, restoring normal operating conditions.
The phenomenon described above corresponds to a night inversion or radiation, which is the most common, although the frontal, marine and subsidence inversion are also remarkable.
In the following animation, you can see how this process occurs.

«The source of this material is the COMET® website at http://meted.ucar.edu/ of the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR), sponsored in part by cooperation agreement(s) with the National Oceanic Administration and Atmospheric (NOAA), US Department of Commerce ((DOC)) © 1997-2017 University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. All rights reserved.”
The presence of this type of temperature inversion is usually easily recognizable since fog or smoke tends to concentrate near the earth’s surface, extending horizontally.
It is also a phenomenon that is felt especially in the valleys, areas where the topography of the terrain makes local atmospheric circulation difficult (Rendón, Salazar, Palacio & Wirth, 2015).
What is the relationship between thermal inversion and pollution?
In the explanation of how a thermal inversion occurs, the impossibility of mixing two layers of air with different densities (a consequence of the different temperature) has already been mentioned. Therefore, it is easy to conclude that one of the main effects caused by this thermal imbalance is that the pollution is trapped without the possibility of dispersing in the atmosphere.
In fact, the stratum with higher temperature acts as a cover on the colder air that is in contact with the ground and in which pollutants concentrate. This situation gives rise to the smog or “pollution beret”, visible from several kilometers around and that usually takes prepared with a descent in the levels of air quality.
ENVIRA is specialized in solutions for the design, installation and monitoring of air quality control networks for the measurement of air pollution.
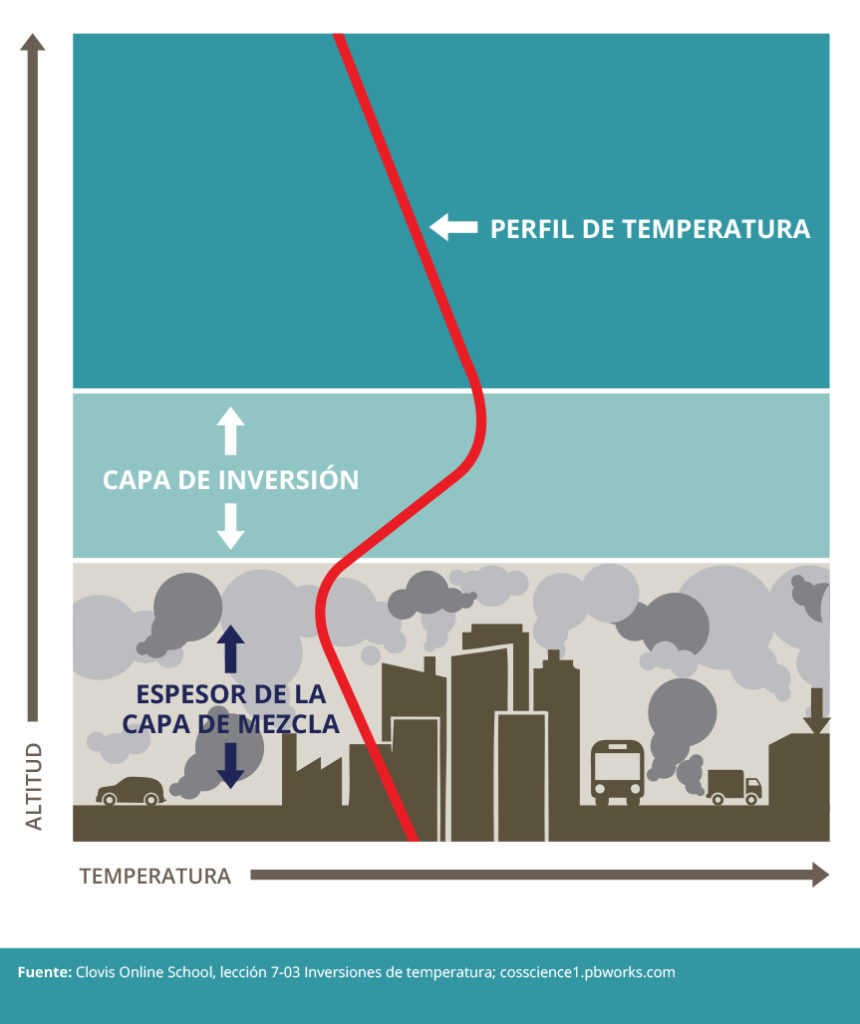
This image has been taken from the European Environment Agency (EEA) CC BY 2.5 DK
The consequences of this phenomenon on human health are translated into an increase in medical consultations motivated by respiratory and cardiovascular problems, especially among the risk groups (children, the elderly and the sick).
This cause-effect relationship was evidenced in the study carried out by Trinh et al. (2018) in Hanoi, a city in which it was possible to verify how the levels of NO2, SO2, PM10 and PM2.5 increased during episodes of thermal inversion, increasing in the same way hospital visits among those under 15 years of age and over 60 years old.
References
- Rendón, A., Salazar, J., Palacio, C., & Wirth, V. (2015). Temperature inversion breakup with impacts on air quality in urban valleys influenced by topographic shading. American Meteorological Society. doi: http://doi.org/f64cx3
- Trinh, T., Trinh, T., Le, T., Nguyen, T., & Tu, B. (2018). Temperature inversion and air pollution relationship, and its effects on human health in Hanoi City, Vietnam. Environmental Geochemistry And Health. doi: http://doi.org/c2mf











