One of the main functions of sensors that has the Internet of Things is the monitoring of the variables of an environment or the factors that determine success in the performance of an activity, such as the control of the operation of a machine in a company.
Today, the levels of monitoring that can be achieved are very broad and cover multiple areas, including from the productivity of a crop to the energy efficiency of a skyscraper. And, most interestingly, more than half of the revenues generated by the IoT after 2020 will be the result of monitoring systems that have not yet been invented. Considering that the sensors and, by extension, the nodes in which they are coupled are a key element in the success of the internet of things, it is worth analyzing what a sensor is and what functions the IoT sensors have.
Anatomy and functions of sensors IoT
A sensor, basically, is a device composed of a transducer, able to detect, measure or indicate changes that occur in a specific physical magnitude (temperature, humidity, pressure, etc.) and transform them into an electrical signal, and a conditioner signal, which amplifies this modification and converts it into an easy-to-read format.
By themselves they are useless, so they usually appear as part of a node, an electronic system in which various components (controllers, power supplies, memory modules, etc.) are connected with each other in order to collect the information, process it and send it through a network.
From the point of view of their functionality, the different applications will be determined by the types of sensors, some of which are collected in the following image, connectivity, power supplies and, occasionally, a user interface (a mobile application, for example).
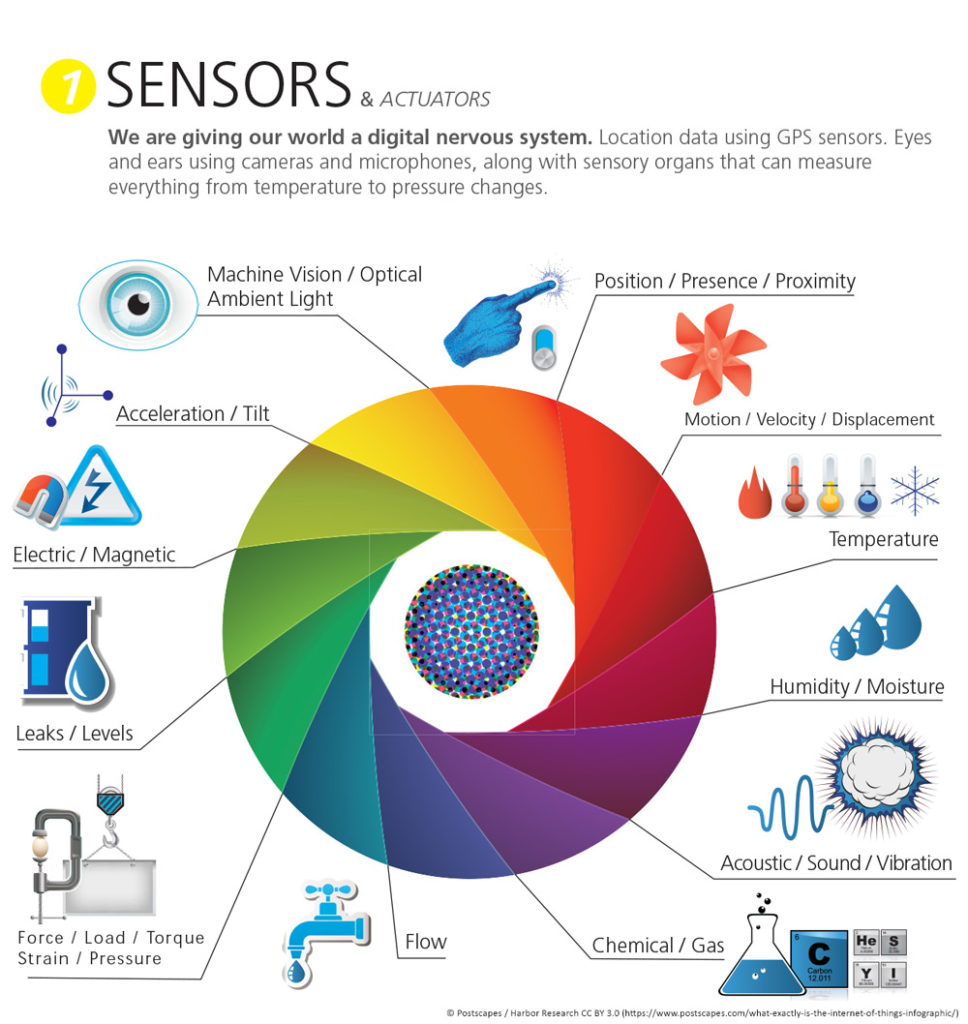
Source: Postscapes / Harbor Research CC BY 3.0 (https://www.postscapes.com/what-exactly-is-the-internet-of-things-infographic/).
What needs do these sensors or nodes satisfy or what problems do they solve? The following sections describe some of the most widely accepted devices
Temperature sensors
As its name suggests, these sensors enable knowing “the amount of thermal energy that allows detecting a physical change in the temperature of a particular source and converting the data for a device or user” (Gorai, 2018).
Temperature sensors have been used massively in air conditioning systems or home appliances, but the development of the internet of things has opened new possibilities for monitoring in areas such as:
- Industrial manufacturing, where certain machines require rigorous temperature control.
- Agriculture, where soil temperature conditions, for example, how plants absorb water.
- Medical technology, with measurement systems, even remote, of patients.
Proximity sensors
The use of these devices is linked to the field of security and surveillance. They detect the presence or absence of a nearby object or the properties of that object, converting them into an easy-to-read signal.
Some practical examples of its use could be sensors installed in vehicles that alert of the presence of objects, devices installed in smart parking or small beacons that improve the experience of buyers with a product in which they are interested by offering discounts.
Gas measurement sensors
Their main function is to monitor the changes that occur in air quality, being increasingly used in urban environments with the aim of providing information on air pollution. To ensure accuracy in the measurement, it is crucial that they are well calibrated, such as those integrated into Nanoenvi EQ equipment, which is subjected to a calibration process in a certified laboratory.
Pressure sensors
These sensors allow the monitoring of the systems and devices powered by pressure. With any deviation from the standard range, the device notifies the presence of a problem to be solved by the system administrator.
Its installation is common in industrial facilities, the maintenance of water supply and heating systems or for obtaining meteorological forecasts.
Humidity sensors
Humidity is defined as the “amount of water, water vapor or any other liquid that is present on the surface or the interior of a body or in the air”.
The sensors that monitor this variable have special importance in areas such as agriculture, for example, where they allow improving the efficiency of irrigation systems, improving the management of a natural resource as scarce as water.
Level sensors
The level sensors are used to measure all types of fluids in liquid, gaseous state, pasty consistency materials, etc.
Their operation is based on measuring the points at which a determined substance is located with respect to the upper edge of a container that contains it, the bottom of it or several reference points.
ENVIRA integrates sensors in devices developed for IoT applications in all sectors and adapted to the needs of each client. For example, the flood monitoring warning system allows the establishment of early warnings and contributes to the prevention of severe damage from flash floods, a phenomenon that, moreover, and as pointed out by various studies, will become increasingly common as a result of the climate change.
References:
- Gorai, S. (2018). Smart sensors slideshare.net Retrieved on January 31, 2019, from https://es.slideshare.net/SupriyaGorai1/smart-sensors-94653798/13











